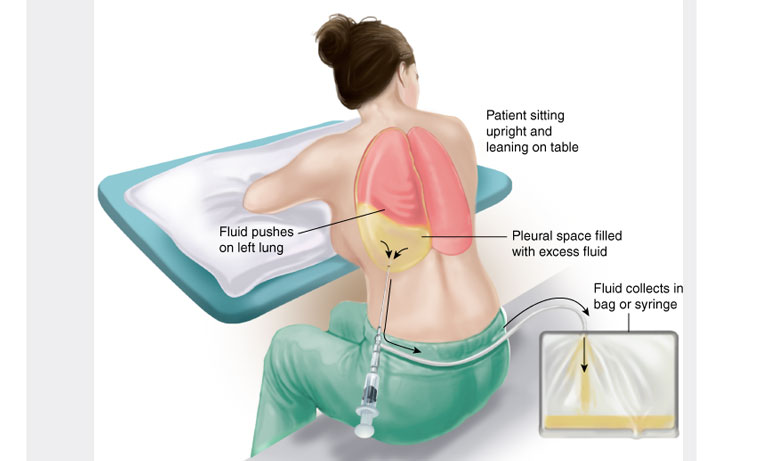
Fluid Tapping
An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. In general, people who have an abscess will experience fever, chills and pain in the approximate location of the area that is involved. If a patient has these symptoms, it is not uncommon that they will undergo an imaging test, (usually a CT scan or an ultrasound), to assist in identifying and making the correct diagnosis of an abscess. Once the diagnosis of an abscess has been made, your physician and an interventional radiologist will work together to decide the appropriate therapy. As long as it is deemed safe, percutaneous abscess drainage offers a minimally invasive therapy that can be used to treat the abscess.
In percutaneous abscess drainage, an interventional radiologist uses imaging guidance (CT, ultrasound or fluoroscopy) to place a thin needle into the abscess to obtain a sample of the infected fluid from an area of the body such as the chest, abdomen or pelvis. Then, a small drainage catheter is left in place to drain the abscess fluid. It may take several days for all the fluid to be removed. Occasionally, abscesses that cannot be treated by percutaneous drainage may require surgical drainage in the operating room.
What are some common uses of the procedure?
Percutaneous abscess drainage is generally used to remove infected fluid from the body, most commonly in the abdomen and pelvis. The abscess may be the result of recent surgery or secondary to an infection such as appendicitis or diverticulitis. Less commonly, percutaneous abscess drainage may be used in the chest or elsewhere in the body.
