Biopsy
Diagnostic techniques, like MRI, Ultrasound, CT or PET, are very useful but in some cases when suspicious tissue (a lesion) is discovered, a doctor may want to get a sample of the suspected cancer. Removal of a sample is called a biopsy.
A biopsy is a sample of tissue taken from the body in order to examine it more closely. A doctor should recommend a biopsy when an initial test suggests an area of tissue in the body isn't normal. Doctors may call an area of abnormal tissue a lesion, a tumor, or a mass. These are general words used to emphasize the unknown nature of the tissue. The suspicious area may be noticed during a physical examination or internally on an imaging test.
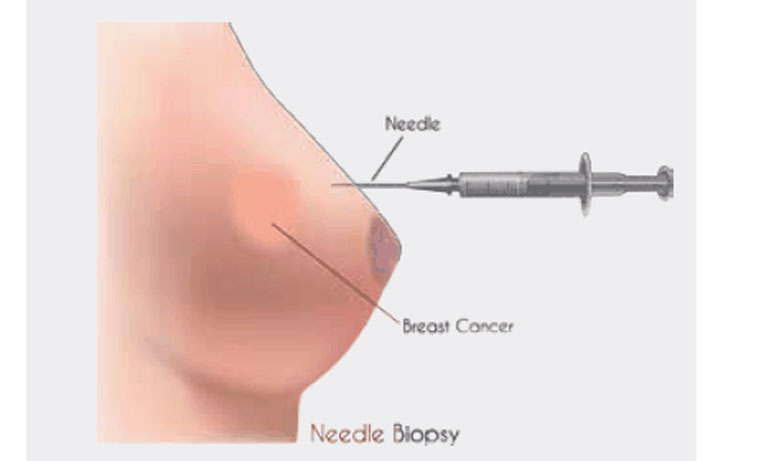
Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNA)
A Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy is a simple procedure that involves passing a thin needle through the skin to sample fluid or tissue from a cyst or solid mass, as can be seen in the picture below. The sample of cellular material taken during an FNA is then sent to a pathology laboratory for analysis. Fine needle aspiration biopsies are often performed when a suspicious lump is found, for example a breast lump or enlarged lymph node, or if an abnormality is detected on an imaging test such as x-ray, ultrasound or mammography. Fine needle aspiration is a relatively non-invasive, less painful and quicker method when compared to other methods of tissue sampling such as surgical biopsy. A cyst aspiration can also be achieved with a FNA, where the fluid is drained from a cyst with no need for analysis.
